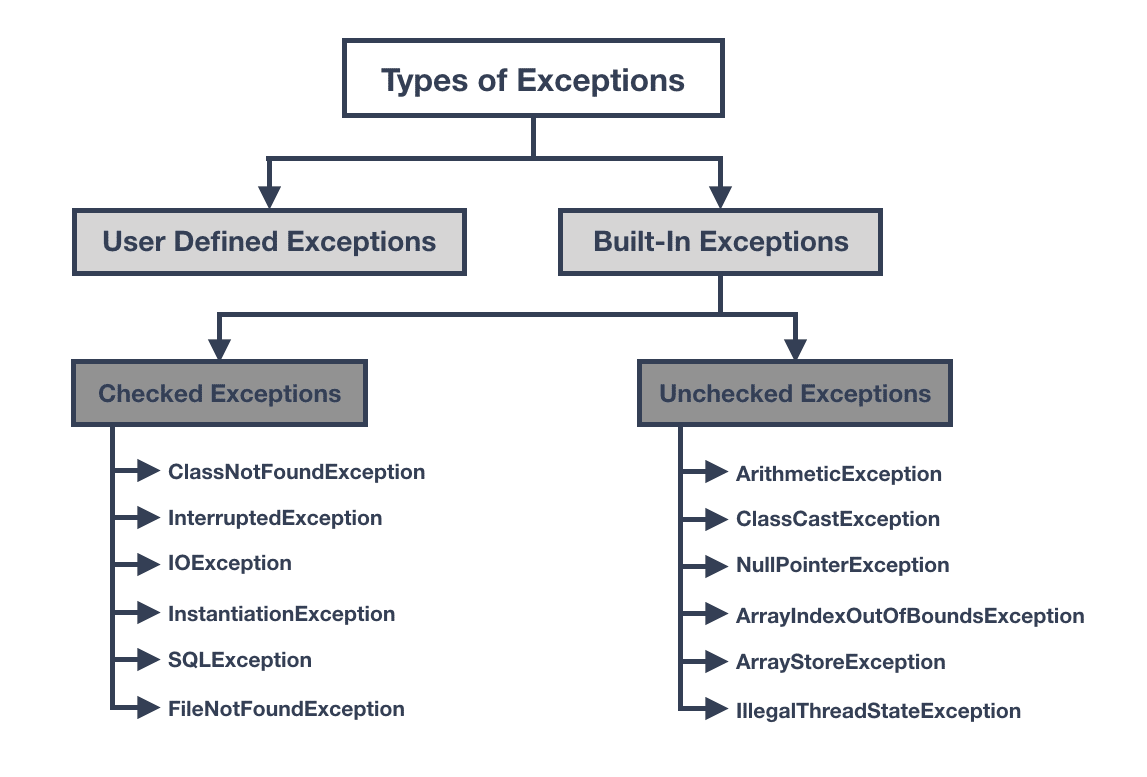
Unchecked Exceptions Are Those That Inherit From
If some code within a method throws a checked exception then the method must either handle the exception or it must specify the exception using the throws keyword. Most of the times these exception occurs due to the bad data provided by user during the user-program interaction.

Course New Java Syntax Lecture Exception Types
What are Unchecked exceptions.
. Only the Error class. There are three simple salient and related facts about catchclauses that we can now fully explore because of our knowledge of inheritanceWe can explain these features in detail here although a naive understanding of them is often enough to do simple exception processing in programs like the standard way that we read files using the. It means if your program is throwing an unchecked exception and even if you didnt handledeclare that exception the program wont give a compilation error.
This answer is not useful. The following code is a constructor for the Book class. The custom exception should extends RuntimeException if you want to make it unchecked else extend it with Exception.
Unchecked exceptions inherit from the Error class or the RuntimeException class. Cause - the IOException. Java Object Oriented Programming Programming.
Show activity on this post. Unchecked exceptions are those that inherit from a. Before going into checked exception Vs unchecked exception lets try to understand which exception classifies as a checked exception and which one as unchecked.
This method may be called from any exception object and it shows the chain of methods that were called when the exception was thrown. For example consider the following Java program that opens the file at location Ctestatxt and prints the first three. In other words classes Error or RuntimeException or those that inherit.
Unchecked Exceptions The Controversy. Many programmers feel that we cannot handle these exceptions in our programs because they represent the type of errors from which. NullPointerException - if the cause is null.
Runtime exceptions can occur anywhere in a program and in a typical one they can be very numerous. RuntimeExceptions should identify programmatically. A catch clause in its header.
Difference Between Checked and Unchecked Exceptions in Java A checked exception is caught at compile time whereas a runtime or unchecked exception is as it states at runtime. These are the exceptions that are checked at compile time. Assume that the classes BlankISBN NegativePrice and NegativeNumberOrdered are exception classes that inherit from Exception.
Exceptions should identify programmatically recoverable problems which are caused by unexpected conditions outside control of code eg. These exceptions inherit from RuntimeException which has the effect. Unlike the checked exceptions the compiler generally ignores the unchecked exceptions during compilation.
The Error class or the Exception class. Both of these shortcuts allow programmers to. 1 If the child is throwing any checked exception then parent must throw only checked exception a Child should throw same exception as parent or b Child should throw any subclass exception of the parent.
What is an Unchecked Exception. So Below program is. Errors should identify programmatically unrecoverable problems eg.
The throws clause causes an exception to be thrown. The Error class or the Exception class. The Error class or the RuntimeException class.
In Java the direct parent class of Unchecked Exception RuntimeException. Only the Error class. Unchecked exceptions are those that inherit from the Error class or the RuntimeException class If a random access file contains a stream of characters which of the following statements would move the file pointer to the starting byte of the fifth character in the file.
Unchecked exceptions are not checked at compile time. Unchecked exceptions are checked during the runtime. The Exception Class or the RuntimeException class.
The Exception Class or the RuntimeException class. These types of Exceptions occur during the runtime of the program. Catch clause is used to handle the exceptions that are thrown by try clause.
Because the Java programming language does not require methods to catch or to specify unchecked exceptions RuntimeException Error and their subclasses programmers may be tempted to write code that throws only unchecked exceptions or to make all their exception subclasses inherit from RuntimeException. View the full answer. Unchecked exceptions are those that inherit from.
In Java exceptions under Error and Runtime Exception classes are unchecked exceptions This Exception occurs due to. Public UncheckedIOException String message IOException cause Constructs an instance of this class. RuntimeException are unchecked while Exception are checked calling code must handle them.
If a method does not handle a possible checked exception what must the method have. We can create the custom unchecked exception by extending the RuntimeException in Java. Because the Java programming language does not require methods to catch or to specify unchecked exceptions RuntimeException Error and their subclasses programmers may be tempted to write code that throws only unchecked exceptions or to make all their exception subclasses inherit from RuntimeException.
Therefore the compiler does not check whether the user program contains the code to handle them or not. A checked exception must be handled either by re-throwing or with a try catch block whereas an unchecked isnt required to be handled. Message - the detail message can be null.
Unchecked exceptions are those that are either Error or RuntimeException. Unchecked exceptions are those that inherit from. Whereas finally clause u.
Catching Exceptions in a Hierachy. Question 6 This is a section of code that gracefully responds to exceptions when they are thrown. Checked exceptions are those exceptions that are of type Exception class Exception and its subtypes except RuntimeException and its subclasses.
These are the exceptions that are not checked at a compiled time by the compiler. Try cause catch clause finally clause throws clause Question 7 Unchecked exceptions are those. In this post well see some of the differences between checked and unchecked exceptions in Java.
The Error class or the RuntimeException class. Straight away diving onto the concept for unchecked exceptions. Unchecked exceptions are those that can be thrown without notice they are not specified in a method signature.
Unchecked exceptions are those that inherit from a the Error class or the from CSCI 1015 at Austin Peay State University. These are exceptions that inherit from the Error class or the RuntimeException class. Well-known examples of unchecked exceptions are ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException IllegalArgumentException or NullPointerException.

Checked And Unchecked Exception Java Developer Central
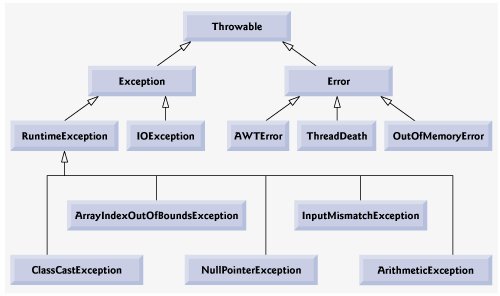
Java Exception Hierarchy Exception Handling

Exception Handling In Java Scaler Topics

Java Why Does Runtimeexception Extend Exception And Not The Other Way Stack Overflow

Solved 1 All Exception Class Inherit From This Class A Chegg Com
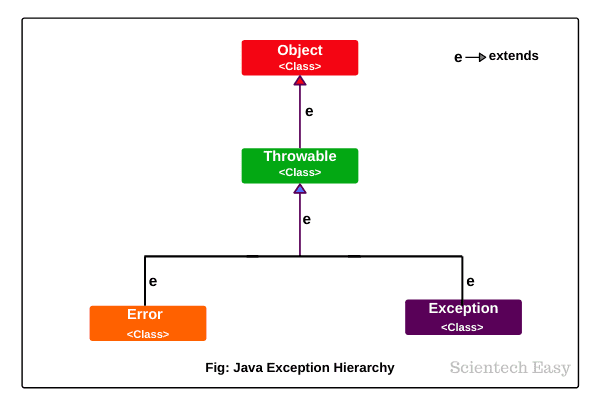
Exception Hierarchy In Java Types Of Exceptions Scientech Easy

How To Handle Checked Unchecked Exceptions In Java Rollbar
Difference Between Checked And Unchecked Exception Difference Between

Java Checked Vs Unchecked Exceptions With Examples

Exception Handling Definition The Term Exception Is Shorthand For The Phrase Exceptional Event An Exception Is An Event Which Occurs During The Ppt Download
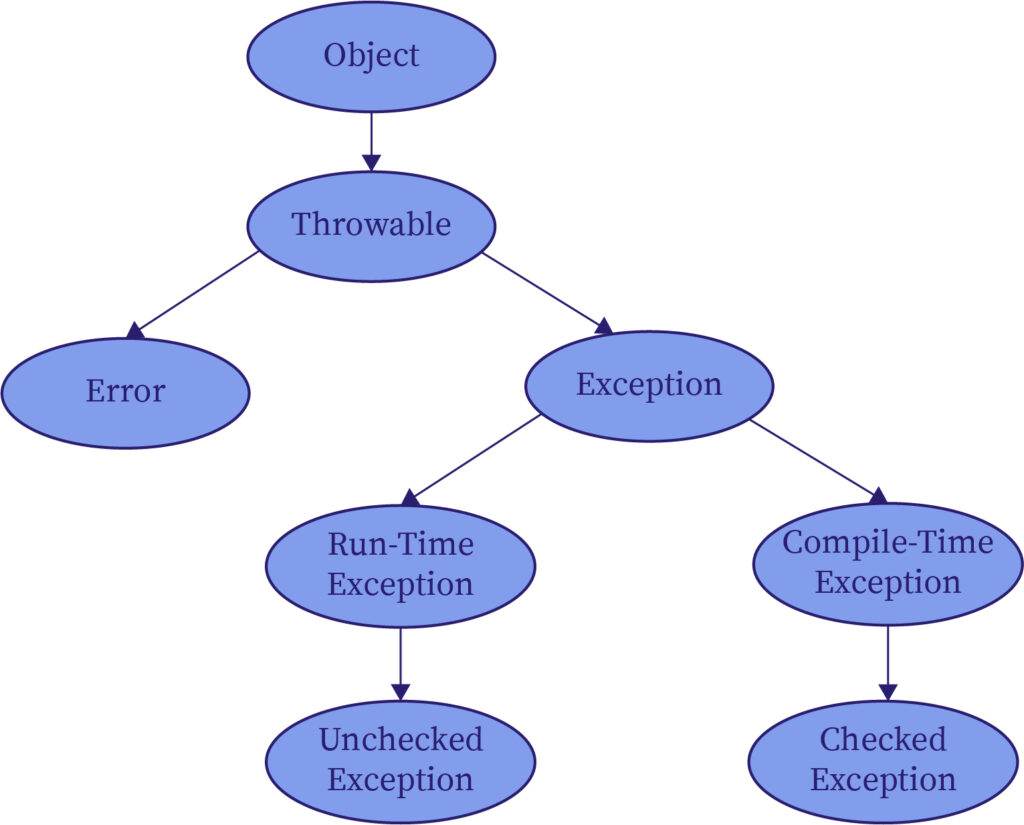
Exception Handling Keywords Bartleby
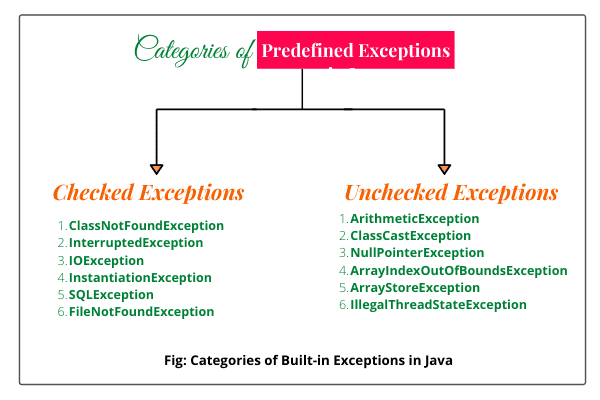
Checked And Unchecked Exceptions In Java Scientech Easy

Exception Handling In Java The Exception Handling In Java Is A By Malshi Madurangi Medium

Java Why Does Runtimeexception Extend Exception And Not The Other Way Stack Overflow

Checked And Unchecked Exception Java Developer Central
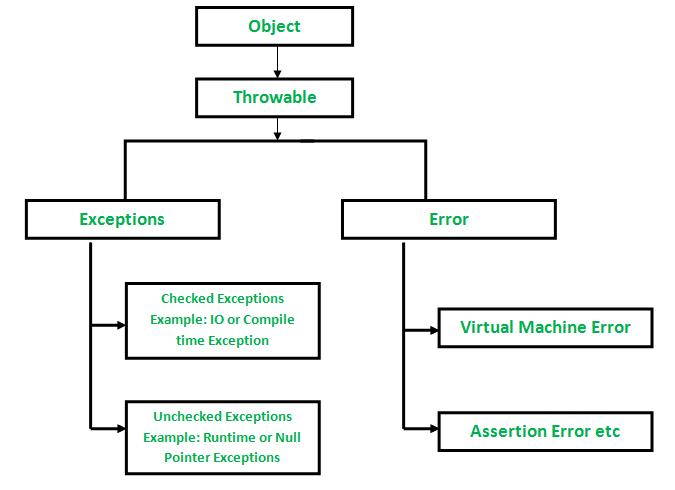
Checked Vs Unchecked Exceptions In Java Geeksforgeeks
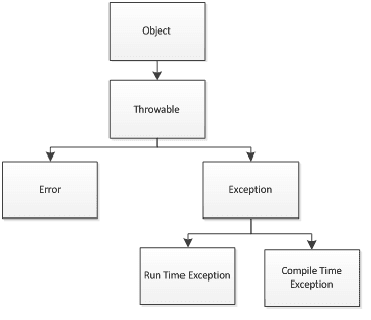
Types Of Exceptions W3resource

How To Identify Checked And Unchecked Exceptions In Java Stack Overflow

Comments
Post a Comment